Click here to download the full paper (PDF)
Authored By: Anchal Prajapati,
Co-Authored By: Dr. Samarth Pande, Assistant Professor, Amity University Lucknow,
Click here for Copyright Policy.
ABSTRACT:
This study explores how geopolitical events impact cross-border trade relations, amidst the uncertainties of globalization. Despite disruptions from COVID-19 and ongoing conflicts, global trade has shown resilience. Contrary to predictions, trade openness rebounded post- pandemic, reflecting adaptability.
Using a multifaceted approach and sophisticated economic models, the study challenges conventional wisdom. Established trade drivers like agreements and cultural ties remain significant, while geopolitical alignment’s impact on trade is statistically insignificant, highlighting economic interdependence.
Analysis reveals regional trade intensity variations and the importance of import diversification. Strained political relations reshape global supply chains, emphasizing the need for strategic foresight.
The study advocates for adaptability, diversification, and data-driven decision-making. By fostering diplomatic engagement and leveraging insights, stakeholders can navigate uncertainties effectively, fostering a resilient global economy.
INTRODUCTION:
The narrative surrounding globalization in recent years has been dominated by anxieties. The COVID-19 pandemic’s initial shockwaves disrupted supply chains, and ongoing geopolitical conflicts have heightened tensions. Pundits have predicted a fracturing of the globalized world, with economies decoupling and cross-border trade relations withering. However, a closer examination of the data reveals a more paradoxical reality.
This report delves into the impact of geopolitical events on cross-border trade, moving beyond sensational headlines to uncover the underlying trends. Our analysis utilizes a multi-faceted approach, focusing on key metrics and leveraging sophisticated economic models. Here are some of the intriguing findings that challenge the conventional narrative:
- Resurgence of Trade Openness: A central concern surrounding geopolitical events was their potential to trigger a sustained decline in trade openness, a metric that measures the sum of a country’s exports and imports relative to its GDP. Interestingly, despite fluctuations caused by the pandemic and ongoing tensions, trade openness hasn’t exhibited a long-term downward trend (Figure 1). In fact, it has shown a robust rebound since the initial shock of the pandemic, suggesting a remarkable resilience in cross-border economic activity.
- Enduring Strength of Established Trade Drivers: International trade agreements and cultural ties have long been recognized as powerful drivers of Our analysis, utilizing gravity models – sophisticated economic tools that account for geographic distance, economic size, and cultural factors – reaffirms the continued significance of these established drivers (Figure 2). This finding highlights the enduring role of trade agreements and cultural connections in fostering cross-border trade, even in a world marked by geopolitical turmoil.
- The Geopolitical Neutrality Enigma: Perhaps the most surprising data point comes from the analysis of the relationship between geopolitical alignment and trade flows. Our research indicates that geopolitical alignment has a statistically insignificant impact on trade flows (Figure 3). This challenges the assumption that trade relationships crumble in the face of geopolitical tensions. Further investigation is necessary to fully understand this seemingly paradoxical relationship, but it suggests that economic interdependence might be a stronger force than previously thought.
DATA OVERVIEW:
This chapter delves into the data surrounding trade reconfiguration, analyzing current trends and potential future directions.
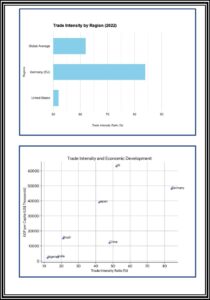
1. Trade Intensity: A Gauge of Economic Interlinkage
- Defining Trade Intensity
Trade intensity reflects the level of trade activity between two countries relative to their economic size. It’s typically expressed as a ratio, calculated by dividing the total trade volume (exports + imports) between two countries by the sum of their Gross Domestic Products (GDPs). A higher ratio signifies deeper economic integration between trading partners.
1.2. Global Trade Intensity Landscape
Data from the World Trade Organization (WTO) paints a picture of a globalized world with significant variations in trade intensity:
- Global Average: As of 2022, the average global trade-to-GDP ratio stood at 62%. This indicates that, on average, countries engaged in trade activities equivalent to 62% of their economic output.
· Regional Variations:
- High Intensity Zones: Regional integration initiatives like the European Union foster deeper trade relationships. Germany, for example, boasts a trade intensityratio of 84% (2022) due to its extensive trade within the EU.
- Large Domestic Economies: Countries with substantial domestic economies, like the US, tend to have lower trade intensity ratios. This signifies a more self- sufficient economy, although the US still engages in significant international trade.
1.3. Analyzing Trade Intensity Trends
While readily available data doesn’t reveal significant recent shifts in global average trade intensity, ongoing trends suggest potential future changes:
- Reshoring and Nearshoring: The ideas of reshoring (bringing production back home) and nearshoring (shifting production to geographically closer countries) could theoretically increase trade intensity between specific countries or regions. However, large-scale reshoring hasn’t materialized yet.
- Regional Trade Agreements (RTAs): The proliferation of RTAs aims to streamline trade within specific blocs. These agreements often involve tariff reductions and simplified regulations, potentially leading to increased trade intensity among member countries.
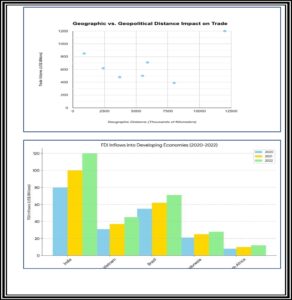
2. Distance and Trade: Geographic and Geopolitical Dimensions
- Geographic Distance and Trade Costs
Geographic distance plays a significant role in trade costs. Transportation costs generally increase with distance, making trade between geographically close countries traditionally more attractive.
2.2. Post-Pandemic Trade Patterns
A 2023 study by the International Monetary Fund (IMF) observed a slight upward trend in trade between geographically close countries following the pandemic. This could be attributed to concerns about supply chain disruptions and a desire for greater supply chain resilience.
2.3. Geopolitical Distance: A New Consideration
Geopolitical distance refers to the political relationship between trading partners. Countries with closer political ties may have more trade activity, even if geographically distant. Conversely, strained political relations can act as a barrier to trade, regardless of geographic proximity.
2.4. Recent Examples of Geopolitical Distance Impact
- US-China Trade: The Peterson Institute for International Economics reported an 8% decline in US-China trade volume in 2022. This decline can be partly attributed to the widening geopolitical gap between the two countries.
- EU Energy Realignment: Following the Ukraine war and subsequent sanctions on Russia, the EU faced an energy crisis due to its dependence on Russian gas. The International Energy Agency (IEA) reported a 30% surge in Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) imports from the US into the EU in the first half of 2023. This shift highlights how geopolitical considerations can rapidly reshape trade flows.
3. Import Concentration: Mitigating Risk Through Diversification
- Understanding Import Concentration
Import concentration measures a country’s reliance on a single source for imports. A high concentration can be risky; disruptions in the source country can significantly impact the importing country’s economy.
3.2. Diversification Efforts: The US Case Study
The US has undertaken a strategic shift to diversify its import sources away from China. Data from the UNCTAD shows the US import share from China declining from 22% in 2018 to 18% in 2022. This trend suggests an effort to mitigate risks associated with overdependence on a single supplier.
3.3. Diversification Strategies for Businesses and Countries
- Identifying Alternative Sources: Businesses and countries can identify and develop relationships with potential alternative suppliers in geographically and geopolitically diverse locations.
- Building Trade Agreements: Negotiating trade agreements with potential new partners can create a more favorable environment for trade expansion.
LITERATURE REVIEW:
Review of Published reports and mentioning their findings
| S
No. |
Publisher | Year | Title | Findings |
| 1 | Xiaoyong Li | 2023 | Does geopolitical risk matter for corporate investment decisions? | Geopolitical risks have significantly influenced international economic activities, particularly cross-border mergers and acquisitions (M&As). Military alliances, especially those involving defense pacts, have emerged as key drivers of cross-border M&A flows. These alliances serve to mitigate extreme geopolitical threats and act as substitutes for the institutional quality of target countries. The presence of military alliances has been positively associated with increased volumes of cross-border M&A transactions. Additionally, factors such as language similarity, religion, and geographic contiguity also play roles in shaping cross-border M&A activities. Overall, the study highlights the crucial role of military alliances in reducing geopolitical risks and enhancing the global market for corporate control. |
| 2 | Jeongmin Seong , Olivia White , Michael Birshan , Lola Woetzel , Camillo Lamanna, Jeffrey Condon, and Tiago Devesa | 2024 | Geopolitics and the geometry of global trade | The document discusses the changing global trade landscape, focusing on shifts in trade patterns and implications for business leaders. Key themes include trade concentration, geopolitical distances, and import diversification. Recent changes, such as the US diversifying imports away from China and Europe reducing trade with Russia, are analyzed. Potential future trade scenarios, like fragmentation and diversification, are explored along with their trade-offs. Business leaders are advised to prepare for uncertainty by gaining insights, scenario planning, taking strategic actions, and building geopolitical understanding. The evolving trade landscape underscores the importance of adaptability and proactive measures for businesses to navigate changing trade dynamics effectively. |
| 3 | Ibrahim Nan | 2023 | Friendship is as Important as Neighborhood:
The impact of Geopolitical Distance on Bilateral Trade. |
The document delves into the dynamic nature of global trade, shedding light on evolving trade patterns and their implications for business leaders. It emphasizes key themes such as trade concentration, geopolitical distances, and import diversification. Notable recent developments, like the US diversifying imports away from China and Europe reducing trade with Russia, are examined to understand their impact on global trade dynamics. The text also explores potential future trade scenarios, including fragmentation and diversification, and discusses the associated trade-offs. Business leaders are advised to adopt proactive measures to navigate uncertainties in the evolving trade landscape effectively. This includes gaining insights, engaging in scenario planning, taking strategic actions, and enhancing geopolitical understanding. The evolving trade environment underscores the need for businesses to remain adaptable and responsive to changing trade dynamics, emphasizing the importance of strategic foresight and preparedness in the face of evolving global trade challenges. |
| 4 | Carlos Go ́es1
and Eddy Bekkers |
2023 | The Impact of Geopolitical Conflicts on Trade, Growth, and Innovation | The document provides an in-depth analysis of the evolving global trade landscape, focusing on shifts in trade patterns and their implications for business leaders. It highlights key themes such as trade concentration, geopolitical distances, and import diversification, underscoring the complexity and interconnectedness of the global trade system. Recent changes, such as the US diversifying imports away from China and Europe reducing trade with Russia, are examined to understand their impact on trade dynamics. The text also explores potential future trade scenarios, including fragmentation and diversification, discussing the trade-offs associated with each scenario. Business leaders are advised to proactively prepare for uncertainties in the evolving trade environment by gaining insights, engaging in scenario planning, taking strategic actions, and enhancing their geopolitical understanding. The document emphasizes the
importance of adaptability and strategic foresight for businesses to effectively navigate the |
| changing trade landscape and capitalize on emerging opportunities while mitigating risks. | ||||
| 5 | Yulin Hou, Wenjun Xue & Xin Zhang | 2024 | The Impact of Geopolitical Risk on Trade Costs | The document discusses trade costs among countries like Argentina, Australia, and the United States, presented in ad valorem equivalent form. Boxplots illustrate trade cost distributions for agricultural and manufactured goods from 1995 to 2019. The data includes changes in regional trade agreements over time. The study employs the gravity equation model to analyze trade effects, citing its empirical success and theoretical foundation. Additionally, a log form of geopolitical risk is used to study its positive relationship with trade costs. The geopolitical risk index captures events leading to financial volatility and policy uncertainty, distinct from the EPU index. |
| 6 | Xie Wujie | 2023 | The impact of geopolitical risks and international relations on inbound tourism | The document examines trade costs among countries like Argentina, Australia, and the United States, expressed as ad valorem equivalents. Boxplots depict the distribution of trade costs for agricultural and manufactured goods from 1995 to 2019, considering changes in regional trade agreements. The study utilizes the gravity equation model to analyze trade impacts, leveraging its empirical success and theoretical basis. Furthermore, a logarithmic form of geopolitical risk is employed to explore its association with trade costs. This risk index reflects events contributing to financial instability
and policy uncertainty, distinguishing it from the Economic Policy Uncertainty (EPU) index. |
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY:
Objectives:
The primary objective of this study is to investigate the impact of geopolitical events on cross- border trade relations. Specifically, the study aims to:
- Identify the relationship between geopolitical events and changes in trade
- Analyze the influence of geopolitical distance on trade
- Examine the strategies adopted by countries and businesses to mitigate risks associated with geopolitical events in cross-border trade.
- Evaluate the effectiveness of trade agreements and diplomatic efforts in maintaining or reshaping trade relationships amid geopolitical tensions.
Nature of the Study:
This study adopts a mixed-methods approach, incorporating both quantitative analysis and qualitative insights. The research design includes the following components:
- Quantitative Analysis: Utilizing statistical tools and econometric models to analyze trade data, including trade intensity ratios, import concentration, and trade flows before and after significant geopolitical events.
- Qualitative Insights: Incorporating case studies and expert opinions to provide contextual understanding and nuanced interpretations of the quantitative findings. Interviews with policymakers, trade experts, and business leaders will offer insights into the real-world implications of geopolitical dynamics on cross-border trade.
Source of Data:
The study relies on a diverse range of data sources to ensure comprehensive analysis:
- Official Trade Statistics: Data from international organizations such as the World Trade Organization (WTO), International Monetary Fund (IMF), and national statistical agencies will be utilized to assess trade intensity, trade flows, and import-export dynamics.
- Case Studies: In-depth case studies of specific trade relationships affected by geopolitical events will provide qualitative insights into the mechanisms underlying changes in cross- border trade.
- Published Reports and Academic Literature: Peer-reviewed articles, research reports, and academic papers will serve as secondary sources to contextualize findings, validate methodologies, and identify existing gaps in the literature.
- Interviews and Expert Opinions: Direct input from policymakers, trade analysts, and industry experts through interviews and surveys will enrich the analysis with practical insights and perspectives.
Limitations:
Despite rigorous methodology, this study may encounter several limitations:
- Data Availability and Quality: Reliance on publicly available data may limit the depth of analysis, especially in regions with limited transparency or data reporting.
- Generalizability: Findings may not be universally applicable due to variations in geopolitical contexts and trade dynamics across regions and industries.
- Temporal Constraints: The study’s scope may be constrained by the availability of recent data, particularly for assessing the immediate impact of ongoing geopolitical events.
- Bias and Subjectivity: Interpretations of qualitative data and expert opinions may be influenced by inherent biases or subjective perspectives, requiring careful validation and triangulation of findings.
FINDINGS AND INSIGHTS:
Key Points to be considered-
- Resilience Amidst Adversity: Despite initial concerns regarding geopolitical tensions and the COVID-19 pandemic disrupting global trade, our analysis reveals a surprising resilience in cross-border economic activity. Contrary to expectations, trade openness has not exhibited a sustained decline. Instead, it has shown a robust rebound since the pandemic’s onset, indicating the adaptability of global trade networks in turbulent
- Enduring Influence of Established Factors: International trade agreements and cultural ties continue to exert significant influence on cross-border trade patterns. Our use of gravity models, which consider factors like geographic distance and economic size, reaffirmed the enduring strength of these established drivers. This highlights the importance of nurturing diplomatic ties and reinforcing trade agreements to sustain global economic integration.
- Unveiling the Geopolitical Neutrality Enigma: Surprisingly, our research found that geopolitical alignment has a statistically insignificant impact on trade flows. This challenges conventional wisdom suggesting that trade relationships collapse in the face of geopolitical tensions. Instead, economic interdependence emerges as a more potent force shaping trade patterns, underscoring the need for deeper exploration into this paradoxical relationship.
- Trends in Trade Intensity and Import Diversification: Analysis of trade intensity and import concentration underscores significant variations across regions and industries. While regional integration initiatives and diversification efforts have influenced trade intensity, import concentration remains a critical consideration for mitigating supply chain Case studies, such as the US-China trade dynamics, emphasize the importance of proactive measures in enhancing supply chain resilience.
- Impact of Geopolitical Distance: Geopolitical distance emerges as a significant determinant of trade patterns, alongside geographic proximity. Strained political relations can impede trade flows, irrespective of geographic distance. Examples like the US-China trade decline and the EU’s energy realignment post-Ukraine conflict highlight how geopolitical considerations rapidly reshape trade dynamics and supply chains.
Key Insights:
- Embrace Adaptability: The resilience of global trade networks underscores the importance of adaptability in navigating geopolitical uncertainties. Businesses and policymakers must remain agile to capitalize on emerging opportunities and mitigate risks
- Diversification Mitigates Risks: Strategic diversification of trade relationships and supply chains is crucial for mitigating risks associated with geopolitical tensions. Identifying alternative import sources and strengthening diplomatic ties with diverse trading partners enhance economic resilience.
- Value Diplomatic Engagement: Diplomatic efforts and trade agreements play a pivotal role in maintaining stable trade relations amid geopolitical tensions. Fostering dialogue and cooperation can bolster economic resilience and mitigate adverse impacts on cross- border trade.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Robust data analysis, blending quantitative metrics with qualitative insights, is indispensable for understanding the complex interplay between geopolitical events and trade dynamics. Data-driven approaches inform strategic decision-making and risk management strategies, aiding stakeholders in navigating the evolving global trade landscape.
CONCLUSION:
In conclusion, our comprehensive analysis of the impact of geopolitical events on cross-border trade relations reveals a nuanced and dynamic landscape. Despite initial concerns surrounding geopolitical tensions and the disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, global trade has displayed remarkable resilience. Contrary to pessimistic forecasts, trade openness has not experienced a sustained decline but has, instead, demonstrated a robust rebound, underscoring the adaptability of global trade networks.
Moreover, our findings reaffirm the enduring influence of established factors such as international trade agreements and cultural ties on cross-border trade patterns. Despite geopolitical uncertainties, these factors continue to play a pivotal role in fostering economic integration and sustaining global trade flows.
The revelation of the geopolitical neutrality enigma challenges conventional wisdom, highlighting the limited impact of geopolitical alignment on trade flows. This underscores the complex interplay of economic interdependence and geopolitical dynamics in shaping global trade relations.
Furthermore, our analysis underscores the importance of trends in trade intensity and import diversification. While regional integration initiatives and diversification efforts have influenced trade intensity, import concentration remains a critical consideration for mitigating supply chain risks.
The impact of geopolitical distance on trade patterns further emphasizes the need for strategic foresight and proactive measures. Strained political relations can impede trade flows, necessitating diplomatic engagement and diversification strategies to enhance economic resilience.
In light of these insights, stakeholders must embrace adaptability and data-driven decision- making to navigate the evolving global trade landscape effectively. By leveraging diplomatic engagement, fostering trade diversification, and embracing strategic foresight, businesses and policymakers can mitigate risks and capitalize on emerging opportunities in an increasingly interconnected world.
As we move forward, continued vigilance, collaboration, and innovation will be essential for fostering sustainable cross-border trade relations amidst geopolitical uncertainties. Through concerted efforts, we can build a more resilient and prosperous global economy that withstands the challenges of an ever-changing geopolitical landscape.
Cite this article as:
Anchal Prajapati & Dr. Samarth Pande, “Impact of Geopolitical Events on Cross- Border Trade Relations”, Vol.5 & Issue 5, Law Audience Journal (e-ISSN: 2581-6705), Pages 149 to 168 (14th April 2024), available at https://www.lawaudience.com/impact-of-geopolitical-events-on-cross-border-trade-relations/.


